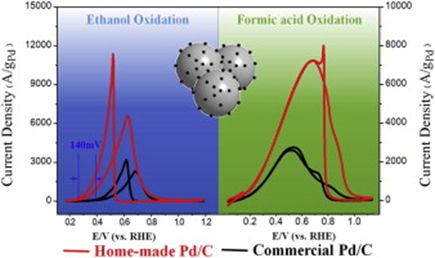
Electrocatalysts of ultrafine and surface-clean nanoparticles uniformly dispersed on high-surface-area conducting supports are among the prime requests for large-scale application of fuel cells. We report a facile one-pot synthesis of carbon-supported monodisperse and ultrafine Pd nanoparticles (Pd/C) in N,N-dimethylformamide by using amine–borane as reducing agent in the absence of any surfactants. The ultrasmall size, monodispersity and surfactant-free surface of Pd nanoparticles make the resulted Pd/C catalyst exhibit excellent electrocatalytic performance toward the oxidation of organic fuels. For formic acid oxidation reaction, it exhibits a similar onset potential to that of the commercial Pd/C (BASF) but about 2.6 times increase in current density, which can be attributed to the increased electrochemically surface area (ECSA); while for ethanol oxidation, it shows about 140 mV negative shift of the onset potential as well as the current increase much beyond that expected by the increased ECSA, indicating that the reduction of Pd particle size not only increases the ECSA, but also enhances the intrinsic activity of surface Pd atoms. The different activity enhancing behaviors for the formic acid and ethanol oxidation have been discussed in terms of the reaction mechanisms. Chronoamperometric measurements show that the home-made Pd/C is also much more durable.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.05.033